Waste to Energy (WtE and EfW)
A Waste to Energy (WTE) plant, also known as EfW (Energy from Waste), is a state-of-the-art waste management facility that transforms non-recyclable waste into electricity while championing environmental sustainability. Through efficient incineration, the WTE plant harnesses heat to produce steam, which powers turbines to generate electricity. This sustainable process not only provides renewable energy but also utilizes excess heat locally, further enhancing its environmental benefits.
Also referred to as energy from waste, municipal waste incineration, energy recovery, or combined heat and power plants, WTE facilities are at the forefront of cleaner energy alternatives. They significantly reduce air pollution compared to traditional coal-fired plants and landfill disposal methods. These innovative plants are carbon-negative, converting waste into fuel with minimal carbon and methane emissions, contrasting sharply with the harmful environmental impact of waste decay in landfills. Embrace this eco-conscious approach to combat climate change and adopt sustainable waste management solutions.
Waste to Energy plants are pivotal in mitigating harmful air pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and particulates commonly found in flue gases. By employing advanced pollution control technologies such as baghouses, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators, these plants effectively filter and capture pollutants. With their integration of high-temperature combustion and efficient scrubbing techniques, waste-to-energy plants make significant strides in reducing air pollution, ensuring a cleaner and healthier environment.
Why Measure?
Environmental concerns
Emissions of acidic gases from various sources are a significant environmental concern, particularly in Waste to Energy (WtE) plants where burning fuel generates HCl (hydrochloric acid) and SO2 (sulfur dioxide) in the flue gas. To mitigate these emissions, absorbers are crucial components within the WtE process. These absorbers, often employing alkaline substances like lime or sodium bicarbonate, chemically react with acidic gases to neutralize them or convert them into less harmful compounds. This process plays a vital role in ensuring that WtE plants operate within strict environmental regulations, minimizing their impact on air quality and public health.
Efficiency
To achieve optimal efficiency of the absorbers in Waste to Energy (WtE) plants, precise control of the entire process is essential. This includes meticulous fuel mixing and accurate measurements that provide crucial feedback to the control room. Additionally, in WtE plants, fuel can be blended in a manner that promotes the generation of HCl in the flue gas at levels conducive to enhancing SO2 absorption in a scrubber. This synergistic approach not only improves the overall efficiency of the absorber systems but also ensures compliance with stringent environmental standards by effectively reducing acidic gas emissions.
Costs
By monitoring the levels of SO2 and HCl at the inlet to the Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) system, controllers gain valuable insights into the process dynamics. This information allows for precise control over the amount of sorbent used, optimizing its dosage and ensuring cost-efficiency by using only what is necessary. This proactive monitoring approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to environmental sustainability by minimizing excess sorbent usage and reducing overall operational costs.
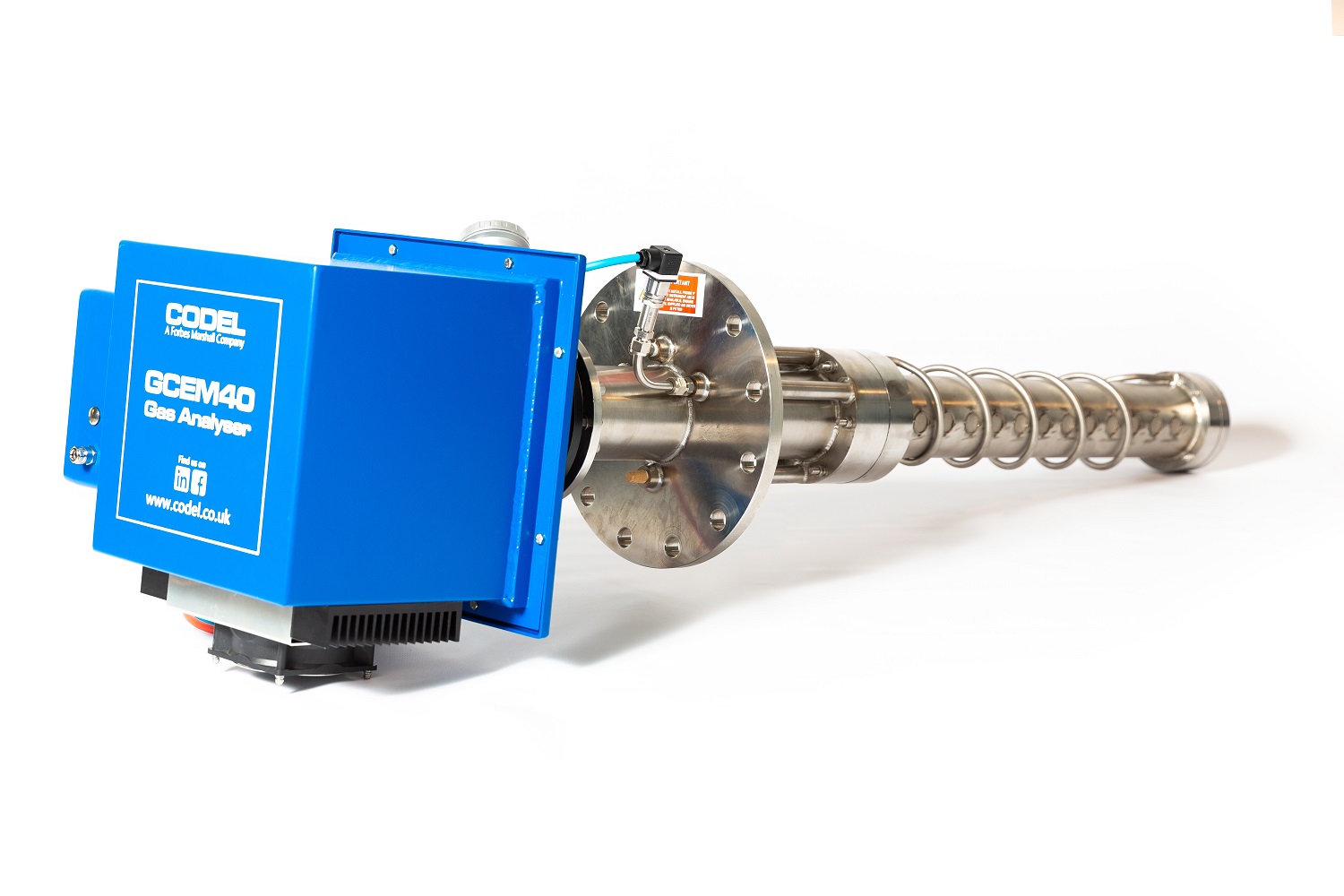
Why CODEL & the GCEM 40?
- Proven & reliable measurement technique – over 1,000 sold worldwide direct from CODEL since its 2009 release and since 2011 a further 1,500 manufactured and sold through Forbes Marshall.
- GCEM 40 Series is a robust analyser, it was designed & built for harsh environments/applications
- Combined SO2, HCL, CO2, H2O, Temp & Pressure all in one analyser, offering optimum accuracy
- Simple & tidy install - 1 probe & head, 1 cabinet
- Minimal maintenance required on a GCEM 40 Series system, results in lower cost of ownership
- Lower initial cost than other measurement options.
- Positive customer feedback
Suitable Products
The GCEM40 analyser is an in-situ device which is cost-effective, low maintenance and designed both for process control and emissions monitoring.
CO, NOx, SO2, HCl, CH4, CO2 & H2O
The GCEM40E hot extractive multi-channel gas analyser is CODEL’s industry-proven continuous emissions monitor for difficult applications
CO, NOx, SO2, HCl, CH4, CO2 & H2O
Ask a question
For further information on any of our products, please complete our enquiry form and a member of staff will respond as soon as possible.
You can also call: +44(0)1629 814351